EAC sees $800m surplus amid intra-States trade surge
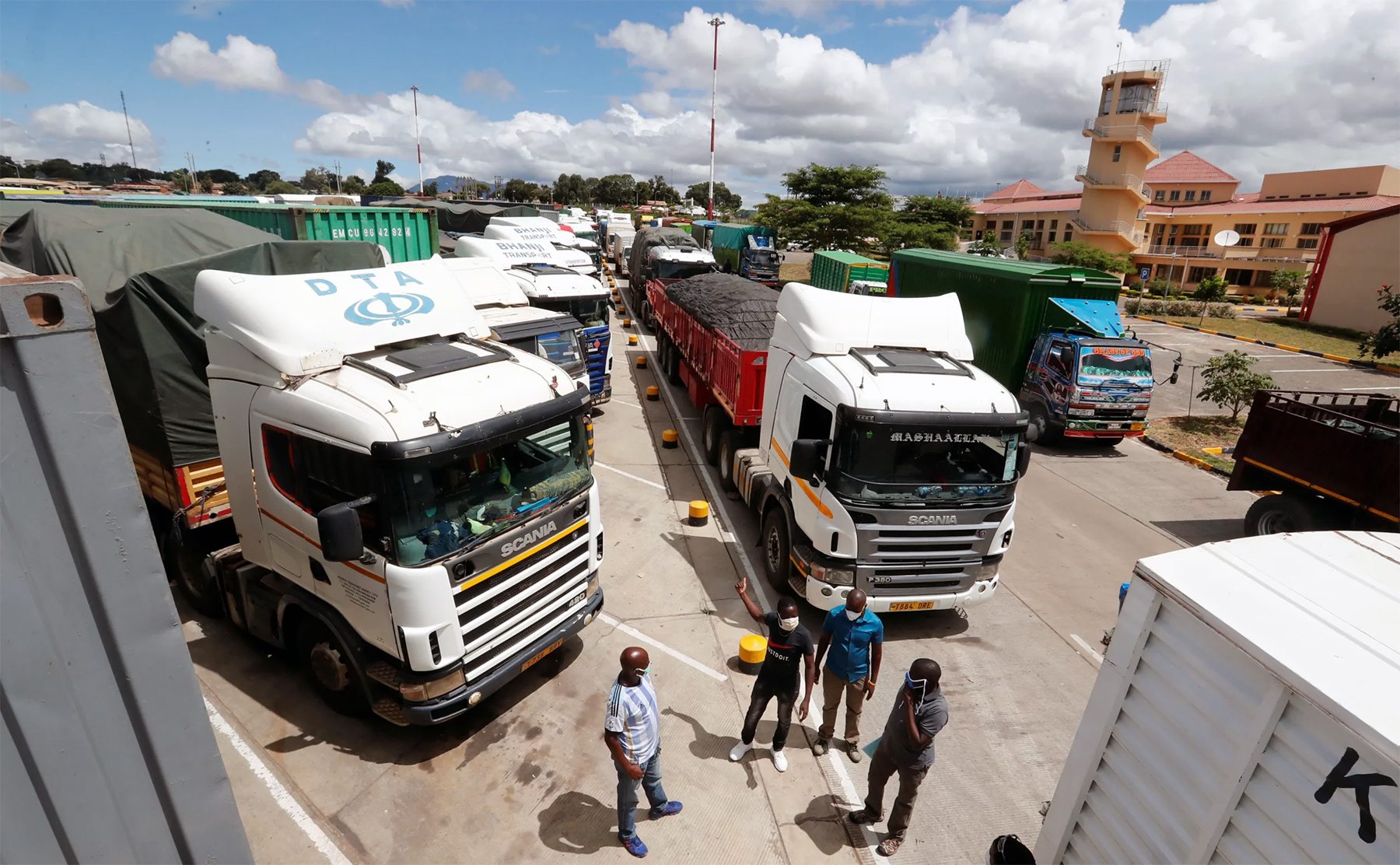

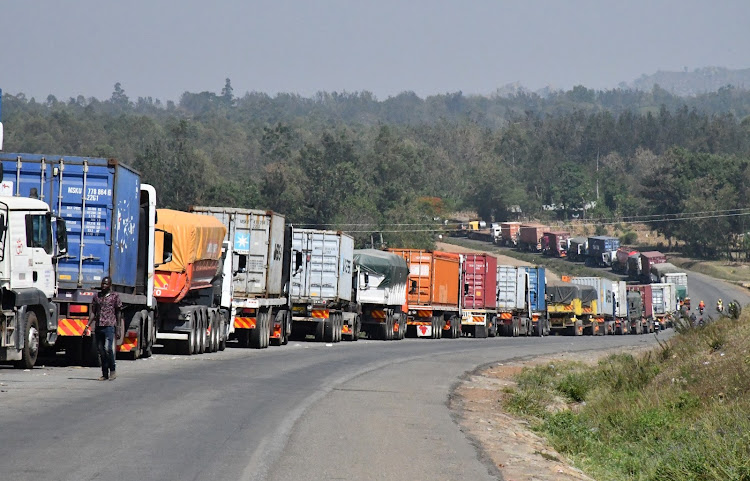
Trucks await clearing at Namanga Namanga One Stop Border Post (OSBP) between Tanzania and Kenya.
The East African Community (EAC) has posted a remarkable economic milestone, registering a trade surplus of USD800 million in the first quarter of 2025.
This represents a dramatic turnaround from the USD 4.0 billion (UGX 15.2 trillion) deficit recorded during the same period in 2024, signalling growing resilience, competitiveness, and economic integration across the bloc.
The EAC Quarterly Statistics Bulletin attributes the surplus to a significant increase in exports, stronger intra-African trade, and improved domestic production capacity.
- Between January and March 2025, the region’s total exports surged by 47.3% to USD 17.7 billion (UGX 67.26 trillion), far outpacing the modest 4.6% rise in imports, which reached USD 16.8 billion (UGX 63.84 trillion).
Domestic exports rose sharply by 48.1%, while re-exports increased by 32.4%, highlighting both higher local production and greater value addition. This performance, the bulletin notes, reflects the success of policy reforms, regional trade agreements, and targeted investments in key sectors.
Intra-African trade emerged as a key growth engine, expanding by 53.9% to USD 9.5 billion (UGX 36.1 trillion) and now accounting for 27.5% of the EAC’s total trade.
- Within the bloc, intra-EAC trade rose by 53.6% to USD 5.2 billion (UGX 19.76 trillion), underscoring progress in dismantling internal trade barriers, harmonising policies, and improving transport infrastructure.


China maintained its position as the EAC’s top trading partner, followed by the United Arab Emirates, India, South Africa, and Japan. Notably, for the first time in recent years, the region recorded a USD 1.8 billion (UGX 6.84 trillion) trade surplus with China, driven by a surge in exports and a slight decline in imports. Other leading export destinations included South Africa, Hong Kong, and Singapore.
Imports continued to be dominated by petroleum products, vehicles, machinery, and plastics. On the export side, trade activity remained concentrated in base metals, minerals, agricultural goods, precious stones, and machinery, which together accounted for more than half of the region’s total trade value.
The report notes that this sectoral concentration underscores the importance of diversifying exports and investing in value addition to enhance global competitiveness.
Despite the strong trade performance, inflationary pressures remain a significant challenge for the EAC’s economies. Regional headline inflation stood at 27.0% in March 2025, down from 30.6% in February but still well above the 6.7% recorded in March 2024.
- Credit to the private sector increased by 5.5%, signalling a gradual recovery in business activity and investor confidence. Sectoral lending patterns showed notable increases in agriculture (6.6%), construction (17.5%), and wholesale and retail trade (9.6%).
- Real estate lending grew by 4.8%, while the manufacturing sector saw only marginal credit growth at 0.5%, highlighting persistent financing challenges for industrial development.
The EAC Secretariat emphasised that the strong Q1 trade results demonstrate the benefits of coordinated trade policies, regional integration, and infrastructure investments. However, it also cautioned that persistent inflation, sectoral dependence on a limited range of exports, and manufacturing sector financing gaps remain areas of concern.
Experts say that to sustain this trade momentum, the bloc will need to focus on diversifying exports, scaling up value addition, and expanding manufacturing capacity. Continued improvements in customs procedures, border efficiency, and transport infrastructure will also be critical to strengthening intra-African trade links.
Compiled in collaboration with national statistics offices and Central banks of the Partner States, the EAC Quarterly Statistics Bulletin remains a key tool for policymakers, investors, and development partners. By providing harmonised macroeconomic data and timely analysis, it supports informed decision-making as the region seeks to deepen integration, boost competitiveness, and navigate an increasingly complex global trade environment.


.jpg)